Scientific achievements of 2015
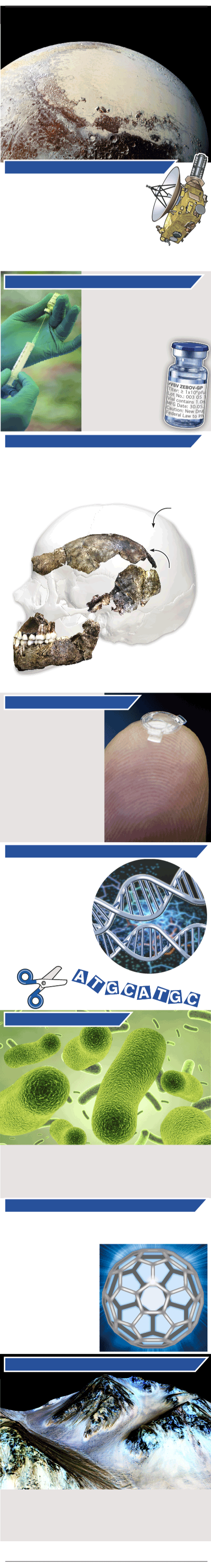
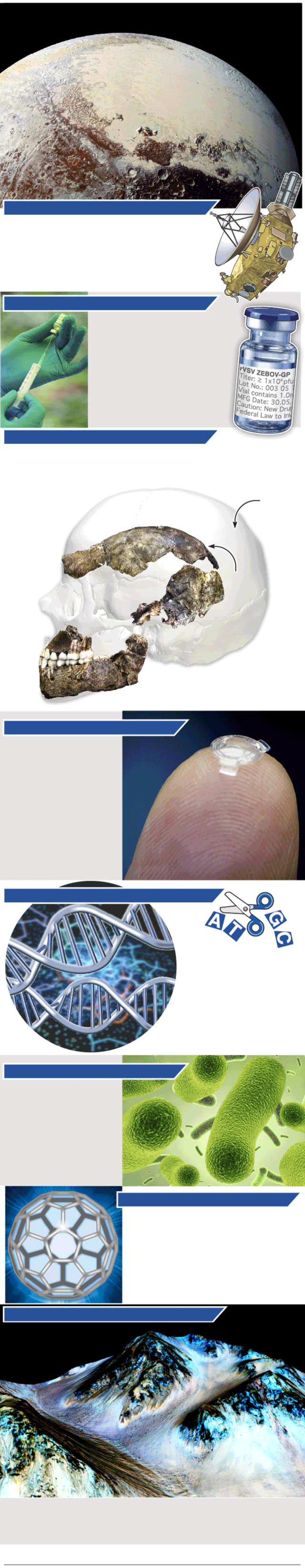
CLOSE ENCOUNTER WITH PLUTO
NASA’s New Horizon spacecraft swoops past distant Pluto, sending back images of ice mountains and frozen nitrogen glaciers flowing at minus 235°C, 38 degrees above absolute zero. The July flyby of the dwarf planet reveals evidence of methane ice, carbon monoxide ice and water ice in the bright Tombaugh Regio area
EBOLA VACCINE BREAKTHROUGH
Following the 2014 Ebola epidemic in West Africa, a clinical trial of Canada’s Public Health Agency’s vaccine, VSV-EBOV, developed by Merck, Sharp & Dohme, leads to 100% protection. The vaccine combines a fragment of the Ebola virus with another, safer virus to train the immune system to beat Ebola
NEW HUMAN ANCESTOR
Fossils of a previously unknown human ancestor are found in a cave in South Africa. Similar to small-bodied humans, Homo naledi adds yet another branch to humanity’s family tree. Homo naledi appears to have buried its dead — behavior previously thought to be limited to humans
Modern
human
Homo
naledi
The braincase of H. naledi measures 560cm³, less than half the volume of a modern human
BIONIC LENS IMPLANT
A new intraocular lens, developed by Ocumetics Technology Corp., enables patients to see three times better than standard 20/20 vision. The procedure, in which the lens inside the eye is replaced with an artificial lens, insertable through a 2.7mm incision, can be done in an outpatient clinic in just eight minutes
CRISPR GENE-EDITING ADVANCEMENTS
Genome-editing technology CRISPR is used in China to modify the DNA of a human embryo. Harvard geneticists use CRISPR to insert genes from an extinct woolly mammoth into lab-grown living cells of a modern elephant
NEW ANTIBIOTIC
Scientists discover a new antibiotic, the first in nearly 30 years, with the potential to treat fatal bacterial infections such as MRSA. Teixobactin works by binding to fatty lipids that form building blocks used by bacteria to build cell walls
NEW STATE OF MATTER
The fundamental states of matter — solid, liquid, and gas — are joined by an exotic new state called Jahn-Teller metal. By inserting the metallic element rubidium into buckyballs — spherical carbon-60 molecules — researchers in Japan have created a crystalline structure that has the properties of an insulator, superconductor and magnet, while acting as a metal
FREE-FLOWING WATER ON MARS
NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter provides evidence of the presence of liquid water on Mars — 100 metre-long streaks of salty water that vary with the seasons. Hydrated perchlorate salts also make the presence of living organisms on the planet more likely
Pictures: Associated Press, Getty Images, NASA/JHUAPL/SwRI, World Health Organisation/S. Hawkey, eLIFE
© GRAPHIC NEWS

